Orange tree, sinensis Citrus
 Etymology: "orange" is an Arab word. "Citrus" comes from a Greek word for "lemon" and "Sinensis" alludes to its Chinese origin. Etymology: "orange" is an Arab word. "Citrus" comes from a Greek word for "lemon" and "Sinensis" alludes to its Chinese origin.
Origin: the orange tree is native to China. It was introduced into Palestine by the Arab caravans, then, from there, imported into Europe by the Crusaders in the XIIth century. Other species are imported by the Portuguese.
Habitat: the orange tree requests a not calcareous and light earth.
Except the Mediterranean coast, French climate is too cold for orange trees and lemon trees. It is necessary to shelter them in winter in a not heated room, but frost free.
Height: 8 m; conical and compact crown becoming spherical due to pruning. The orange tree is smaller than Sour Orange which resembles to it.
Barely rough or grey, smooth bark.
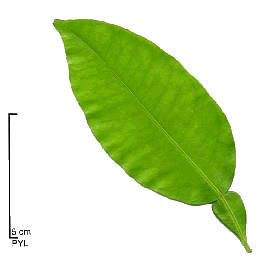
Leaves alternate and persistent, oval, pointed, glazed. They have the feature of a winged petiole (flat and broad). Leaves and orange skin secrete a sweet-scented essential oil.
White flower, with 5 petals. It blooms in the axil of leaves. Self-fertile, the orange tree does not need another tree to be pollinated and to give fruits from the first year. 
The fruit of the Citrus sinensis is called soft orange and is edible. It distinguishes itself from some bitter orange or bigarade, fruit of the aurantium Citrus. It is a citrus fruit. It contains many seeds and drift of an unique ovary. The districts of the orange are carpels. They contain the pips which are seeds, that contain several sprouts to some species (mandarin tree, kumquat).
Uses and varieties: the orange is edible. Varieties with harvest in March-April and in December, as well as blood variety due to the presence of anthocyanoside are differentiated. The XVIIIth century invents "orangeries" to keep young plants in winter, because they do not support frost.
Advices of maintenance:
The orange tree grows very well in a pot. It would be good to repot every year to regenerate the land. For the benefit of adding farmyard manure (purchased in bag dehydrated) or fertilizer (not too much nitrogen but potassium). Well sprinkle especially during flowering.
About pruning: prune them when they have flowers, just above above clusters, so that the sap concentrates to fabricate fruits. When there are fruits, cut the green stems and the leaves above fruits so that the fruits grow and do not fall.
|